-
- Las palabras y oraciones en inglés
- Los tipos de palabras esenciales para hablar inglés
- La estructura de oraciones en inglés
- Los pronombres personales
- El presente simple
- El presente simple
- Oraciones negativas en el presente simple
- Preguntas en el presente simple
- El verbo "be"
- El pasado simple
- El pasado simple
- Verbos irregulares en el pasado
- Pasado simple negativo e interrogativo
- "Be" en el pasado
- El futuro y verbos auxiliares
- El futuro simple
- Verbos auxiliares
- El presente continuo y perfecto
- El presente continuo
- El presente continuo para expresear el futuro
- El presente perfecto
- Contractions
- Adjetivos, adverbios y preposiciones
- Los adjetivos
- Los adverbios
- Las preposiciones
- Preposiciones de lugar
- Preposiciones de tiempo
- Los artículos
-
- Module 1
- There is - There are
- El comparativo
- El superlativo
- El imperativo
- Gerundios
- Question tags
- For, Since, Ago
- Have you ever...? How long have you...?
- Used to, be used to, get used to
- Used to vs would
- Have to vs Must
- I'd like y would you like?
- El pronombre "it"
- Too / Either, So am I / Neither am I
- Reported Speech
- La voz pasiva
- Expresar propósito
- I want you to... I told you to...
- Adjetivos y Pronombre Posesivos - Apostrophe 's
- Pronombres reflexivos
- Contables y No Contables
- This, That, These, Those
- One, Ones
- Collocations
- Adjetivos con -ed vs -ing
-
- Pronombres avanzados
- Some y Any
- Pronombres indefinidos
- No, None y Any
- All y Every
- Both, Either, Neither
- Cantidad y comparaciones
- Much, Many y A lot of
- A little y A few
- Not as...as
- Give me that book vs Give it to me
- Good at, Bad at
- Tiempos verbales avanzados
- Cuándo usar el presente perfecto
- Presente perfecto continuo
- Pasado continuo
- Pasado Perfecto
- Pasado perfecto continuo
- Verbos auxiliares
- will vs shall
- Will vs going to
- Will be doing vs will have done
- Can, could, be able to
- must vs can't
- May vs Might
- Los condicionales
- Zero conditional
- First Conditional
- Second Conditional
- Third conditional
- Introducción a los Phrasal Verbs
-
Premium
- Module 1
- Phrasal Verbs Upper intermediate
- Have to vs Must Upper intermediate
- Could have, should have, would have
- Should vs Must
- Have vs Have got
- Had better vs It's time
- Mixed conditionals Upper intermediate
- If I had known vs I wish I had known
- The Passive Voice
- have something done
- Verb + to vs Verb + ing
- Verbs that must be followed by ing
- Verbs that must be followed by to
- Prefer vs Would Rather vs Would Prefer
- No point in vs Not Worth
- When to use "the"
- Possessives 's' vs 'of'
- "Of mine" vs "My own" vs "On my own"
- There and It
- Each vs Every
- Relative clauses with who/which/that
- Relative clauses without who/which/that
- Relative clauses with whose, whom and where
- Advanced Relative Clauses
- Participle clauses
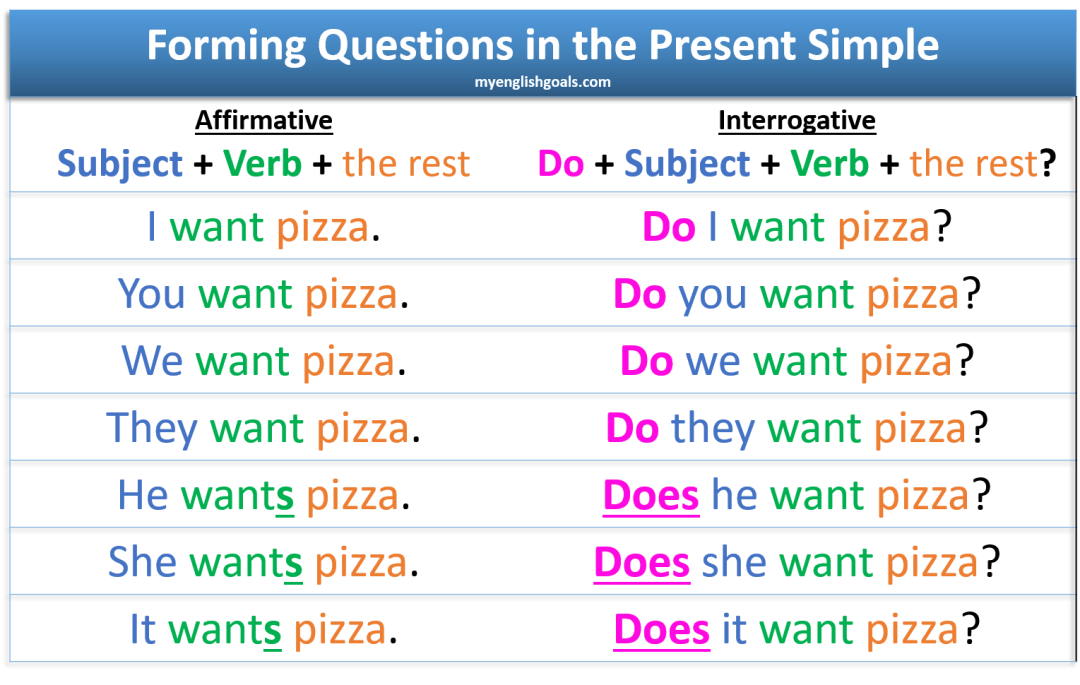
Preguntas en el presente simple
El verbo auxiliar para formar preguntas
Usamos el verbo auxiliar "do" para formar preguntas en inglés.
Aprendiste el verbo auxiliar "don't" en la lección anterior sobre oraciones negativas. Siempre ponemos los verbos auxiliares después del sujeto en oraciones afirmativas y negativas.
Pero en preguntas siempre ponemos el verbo auxiliar antes del sujeto.
Así convertimos una oración afirmativa a una pregunta:

Amazon Fire TV 50" 4-Series 4K UHD smart TV, stream live TV without cable
$269.99- You eat pizza. => Do you eat pizza?
Comes pizza. => ¿Comes pizza? - They walk to school. => Do they walk to school?
Caminan a la escuela. => ¿Caminan a la escuela?
El verbo auxiliar para "he", "she", "it"
Con "he", "she" y "it" usamos el verbo auxiliar "does".
- He runs. => Does he run?
Él corre. => ¿Él corre? - It works. => Does it work?
Funciona. => ¿Funciona?

Roku Streaming Stick 4K | Portable Roku Streaming Device 4K/HDR/Dolby Vision, Roku Voice R...
$39.00Fíjate que no decimos "Does he runs" ni "Does it works". El verbo no se conjuga cuando usamos verbos auxiliares, por lo tanto estos verbos no llevan "s".
Aprenderás sobre los varios verbos auxiliares en inglés en otras lecciones.
Palabras de pregunta
Las típicas palabras de preguntas son:

Hisense 50-Inch Class R6 Series 4K UHD Smart Roku TV with Alexa Compatibility, Dolby Visio...
$999.00- What (qué)
- When (cuándo)
- Where (dónde)
- Who (quién)
- Why (por qué)
- How (cómo)
Estas palabras van al inicio de las preguntas. Por ejemplo:
- What do you want?
¿Qué quieres? - When do you sleep?
¿Cuándo duermes? - Where do you shop?
¿Dónde compras? - Who do you like?
¿Quién te gusta? - Why do you sing?
¿Por qué cantas? - How do you know?
¿Cómo lo sabes?
Haz al menos 2 ejercicios para completar esta lección

Taco Cat Goat Cheese Pizza
$9.84
 Diario
Diario